Science → Solar Cells → How a PV System Works
PV systems are similar to other electrical power generating systems in term of operation and integration but different in term of equipment used for conventional electromechanical generating systems. PV array produces power when exposed to sunlight that required many components to conduct properly, control, convert, distribute, and store the solar energy.
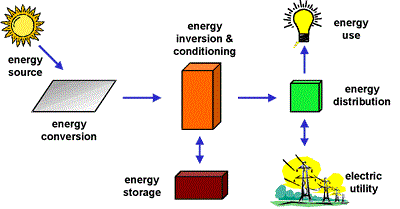
Depending on the type of system, major components may include a DC-AC power inverter, storage battery, battery-controller, auxiliary energy sources, and sometimes the specified electrical load (appliances). Figure bellow shows a basic diagram of a photovoltaic system and the relationship of individual components.
Why Batteries Are Used in Some PV Systems?
Batteries are used in PV systems for the purpose of storing energy produced by the PV array during the day, and supply it to electrical loads as needed during the night time and the cloudy conditions. Batteries are also used to operate the PV array at the maximum power point, at the stable voltage, and to supply surge currents to electrical loads and inverters. In most cases, a battery charge controller is used in these systems to protect the battery from overcharge and over-discharge.
Next: Types of PV Systems