Exponential Growth Law
Let P be the initial amount deposited in an account, and let A be the amount in the account at any time t. In Continuous Compound Interest we notice that rate of growth of A is proportional to A.
Mathematically,
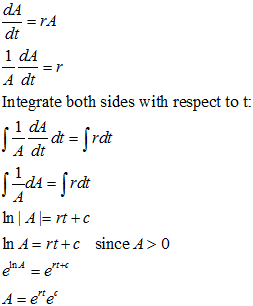
Applying initial condition, when t = 0 and A = P
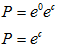
By putting ec = P in the above equation, we have
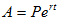
This is same, as the Continuous Compound Interest Formula.
In general, if the rate of change of a quantity Q is proportional to the amount present Q(0) = Q0 at any time t, we obtain the Exponential Growth Law, as:
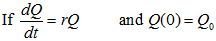
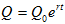
This is called the Exponential Growth Formula.
Where,
Q0 = Quantity at t = 0 (Initial Quantity)
r = Continuous compound growth rate
t = Time
Q = Quantity at time t
NOTE: If r < 0, then dQ/dt < 0 and Q is decreasing. This type of growth is called Exponential Decay.
Example 1. The number of internet connections in Pakistan are estimated as 4 million in 2013, and the growth rate is 1.5% per year. Find the number of internet connections in Pakistan in 2020.
Solution:
Here, Q0 = 4 million (initial quantity), r = 1.5% (0.015) and t = 7 (2020-2013=7)
As we know that the formula for exponential growth is:
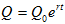
Hence,
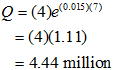
|
Basic Financial terms in Corporate and Mathematical Finance |
Selection of assets, risk and return, and portfolio analysis |
View the online notes for Financial Mathematics (CT1) |
Learn Financial Computing with C++ step by step |