Science → Solar Cells → Wafers, Modules & Arrays
A wafer is a thin slice of semiconductor material, such as crystalline silicon (99.9999999% purity), which used in electronics for the fabrication of integrated circuits and photovoltaics for conventional, wafer-based solar cells.
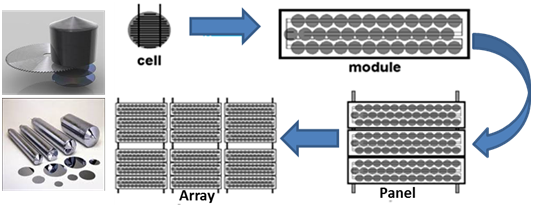
A number of solar cells electrically connected to each other in series or parallel circuits to produce higher voltages, currents and, power levels and mounted in a support structure or frame is called a photovoltaic module. Photovoltaic modules consist of series of interconnected PV cell circuits sealed in an environmentally protective cover, and are considered as a fundamental building blocks of PV systems. PV panels include one or more PV modules assembled as a pre-wired, field-installable unit. A PV array is a complete power generating unit, consisting of some PV modules and panels.
The current produced is directly dependent on a strength of light strikes on the module. In general, the larger the area of a module or array, the more electricity will be produced. PV modules and arrays provide direct-current (dc) power.
The performance of PV modules and arrays is rated according to their maximum DC power output (watts) under Standard Test Conditions (STC). STC is defined by a module (cell) operating temperature of 25oC (77oF), under Air Mass* 1.5 spectral distribution, and incident solar irradiance level of 1000 W/m2. Since these conditions are not always the same, actual performance is usually 85 to 90 percent of the STC conditions.
Nowadays photovoltaic modules are extremely safe and reliable, with minimal failure rates and service times of 20 to 30 years. Many manufacturers offer warranties of 20 or more years for maintaining a high efficiency. When selecting PV modules, always look for the product listing (UL), qualification testing, and warranty information in the module manufacturer’s specifications.
*Note: The air mass coefficient is a direct optical path length through the Earth’s atmosphere. It is expressed as a ratio relative to the path length vertically, i.e. at the top. The air mass coefficient can be used in the characterization of the solar spectrum after solar radiation has traveled through the atmosphere. The air mass ratio is commonly used to describe the performance of solar cells under standard conditions and is represented as “AM” followed by a number. “AM1.5” is almost universal when characterizing terrestrial power-generating panels.
Next: How a PV System Works