Mathematics → Subject Test → Cayley-Hamilton Theorem
Definition
Cayley-Hamilton Theorem states that every square matrix satisfies its own characteristic equation.
That is, if p (λ) = det ( A – λI ) is the characteristic polynomial of the matrix A, then according to Cayley-Hamilton Theorem p ( A ) = 0
For example,
If p (λ ) = det ( A – λI ) = λ2 – λ15 + 56 is the characteristic polynomial, then by Cayley-Hamilton Theorem A2 – 15 A + 56 I = 0
The following examples will make the matter more clear.
Practice Problems
Example 1. If
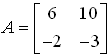 then show that A3 = 7 A – 6 I
then show that A3 = 7 A – 6 I
Solution
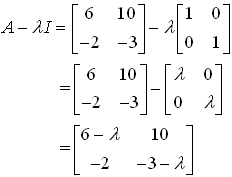
the characteristic polynomial of A is
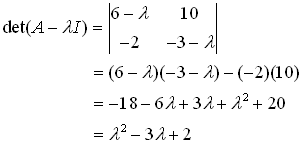
Now, by Cayley-Hamilton Theorem
A2 – 3 A + 2 I = 0 ——> (1)
From (1): A2 = 3A – 2 I
multiply A on both sides of above equation
A3 = 3A2 – 2A ——–>(2)
Put A2 = 3A – 2 I in equation (2)
(2)⇒ A3 = 3 ( 3A – 2 I ) – 2A
A3 = 9A – 6 I – 2A
A3 = 7A – 6 I Answer
Example 2. If
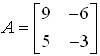
then show that A5 = 981 A – 540 I
Solution
The characteristic polynomial of A is
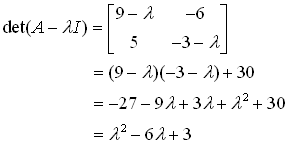
Now, by Cayley-Hamilton Theorem
A2 – 6 A + 3 I = 0 ——> (1)
From (1): A2 = 6 A – 3 I
multiply A on both sides of above equation
A3 = 6 A2 – 3 A ——–>(2)
Put A2 = 6 A – 3 I in equation (2)
(2)⇒ A3 = 6 ( 6 A – 3 I ) – 3 A
A3 = 36 A – 18 I – 3 A
A3 =33 A – 18 I
multiply A2 on both sides of above equation
A5 = 33 A3 – 18 A2 ——–>(3)
Put A2 = 6 A – 3 I and A3 =33 A – 18 I in equation (3)
(3)⇒ A5 = 33 ( 33 A – 18 I ) – 18 ( 6 A – 3 I )
A5 = 1089 A – 594 I – 108 A + 54 I
A5 = 981 A – 540 I Answer