Public debt (also known as Government debt) is the debt owed by federal government. Pakistani government borrows by issuing securities, bonds, and from financial institutions such as Asian Bank, World Bank and IMF. Pakistan’s public debt has two main components:
- Domestic debt which is incurred principally to finance fiscal deficit, and
- External debt which is raised primarily to finance development expenditure.
Pakistan’s Debt-to-GDP ratio was increased from 60.2% in 2013 to 61.4% in 2017. Find some explanation of Pakistan’s debt by clicking here.
Recent History of Pakistan’s Public debt (Rs. in billion)
| Year | Domestic Debt | External Debt | Public Debt |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 6,017 | 4,750 | 10,767 |
| 2012 | 7,638 | 5,057 | 12,695 |
| 2013 | 9,522 | 4,797 | 14,318 |
| 2014 | 10,920 | 5,071 | 15,991 |
| 2015 | 12,199 | 5,182 | 17,381 |
| 2016 | 13,627 | 6,051 | 19,678 |
| 2017 | 14,855 | 6,552 | 21,407 |
| 2018 | 15,437 | 7,382 | 22,820 (Dec 2017) |
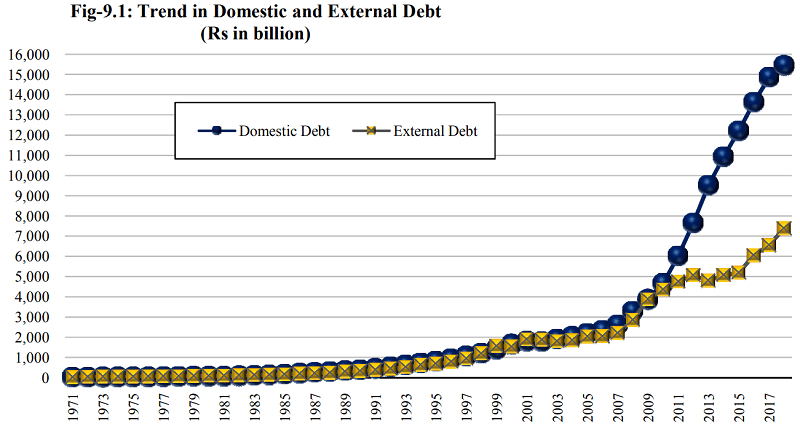 Figure 1. Trend in Domestic and External Debt
Figure 1. Trend in Domestic and External Debt
Public Debt to GDP Ratio
An important measure regarding public debt is Public debt to GDP ratio, that is how much a country owed with respect to its GDP.
Recent History of Public Debt to GDP Ratio
| Year | Net Debt-GDP Ratio | Gross Debt-GDP Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 54.3% | 58.9% |
| 2012 | 59.3% | 63.3% |
| 2013 | 60.2 % | 64.0% |
| 2014 | 58.1% | 63.5% |
| 2015 | 58.3% | 63.3% |
| 2016 | 61.3% | 67.7% |
| 2017 (Dec 2017) | 61.4% | 67.0% |
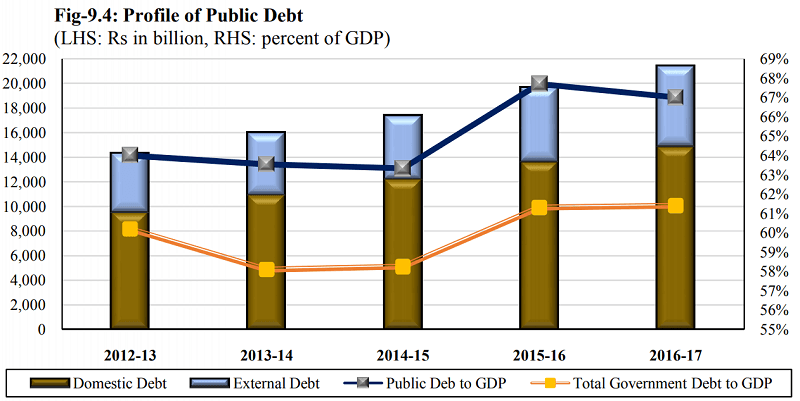 Figure 2. Public Debt to GDP Ratio
Figure 2. Public Debt to GDP Ratio
The table below shows Pakistan’s debt-to-GDP ratio in comparison with some other countries.
| Country | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 81.5 | 80.9 | 80.5 | 81.4 | 82.4 |
| United Kingdom | 77.7 | 79.6 | 80.4 | 80.7 | 80.4 |
| Japan | 117.3 | 118.9 | 118.3 | 119.7 | 119.9 |
| India | 68.5 | 68.5 | 69.5 | 69.5 | 67.7 |
| Srilanka | 70.8 | 70.7 | 76.0 | 77.3 | 79.5 |
| Egypt | 73.7 | 77.1 | 78.8 | 88.1 | 93.6 |
| Pakistan | 60.2 | 58.1 | 58.3 | 61.3 | 61.4 |
Find some explanation of Pakistan’s debt by clicking here.