Black-Scholes Model
The Black-Scholes-Merton model is a model to price European-style stock options. The model assumes that the stock price follows Geometric Brownian motion (also called exponential Brownian motion)
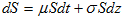
where 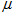 is stock's expected rate of return,
is stock's expected rate of return, 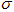 is the volatility of the stock price, and dz is the Wiener process (also called standard Brownian motion).
is the volatility of the stock price, and dz is the Wiener process (also called standard Brownian motion).
Black, Scholes and Merton 1973 created a riskless portfolio of the option and stock to eliminate the Wiener process from the above equation, and obtained Black-Scholes-Merton partial differential equation
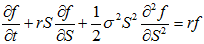
where f is the value of an option.
Final and Boundary conditions
The European call option gives the payoff S-K at t=T when S>K and is worthless otherwise, so the final condition is
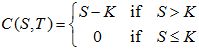
The option is worthless, that is, C(0,t)=0 when S=0. And, when the asset price increases without bound, that is, 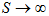 , the exercise becomes less and less important. Hence, the boundary conditions are
, the exercise becomes less and less important. Hence, the boundary conditions are
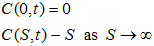
The solution to the Black-Scholes-Merton partial differential equation with these final and boundary conditions is called Black-Scholes-Merton formula for European-style call option
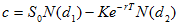
Using put-call parity for European option

We can obtain the formula for European put option
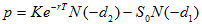
Where
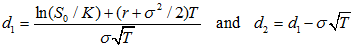
|
Basic Financial terms in Corporate and Mathematical Finance |
Selection of assets, risk and return, and portfolio analysis |
View the online notes for Financial Mathematics (CT1) |
Learn Financial Computing with C++ step by step |